Common Symptoms
Each separate type of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome has its own specific list of symptoms, but many of the symptoms are common across the types. This list covers many of the symptoms or associated syndromes that may be present in individuals with any type of EDS.
-
Cutaneous manifestations
-
Skin hyperextensibility
-
Skin can easily be pulled away from the body and goes back to normal after it is released
-
-
Skin fragility
-
Easily damaged especially on the elbows, knees, forehead, chin, and shins
-
Sutures may not hold and can often tear through the skin
-
-
Delayed wound healing
-
Wounds may take longer to heal due to the wound pulling apart during the healing process
-
-
Abnormal scarring
-
Scars may become widened and atrophic (recessed) or keloid (raised), or take on a cigarette-paper appearance
-
Molluscoid pseudotumors (fleshy lesions associated with scars) may develop where there are scars over bony pressure points
-
-
Soft, thin, translucent skin
-
Poor response to local anesthetic
-
-
Musculoskeletal manifestations
-
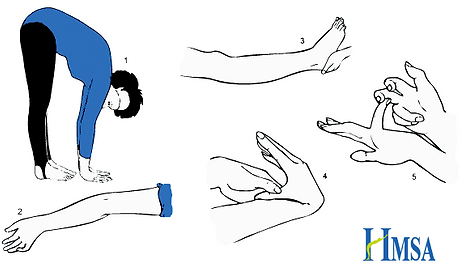
Joint hypermobility can lead to frequent injuries of the joints including sprains, subluxations, and dislocations
-
Subluxations and dislocations frequently affect, but are not limited to, small joints of the hands and feet, and the shoulders, hips, and knees
-
Dislocations and subluxations can occur spontaneously or within normal range of motion and can usually be reduced (put back in place) by the patient
-
Chronic, widespread musculoskeletal pain is a common symptom among patients with classic EDS
-
Joints may be unstable due to joint hypermobility and may cause problems with everyday activities
-
Flat feet (pes planus) is common
-
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) problems are common
-
Joint hypermobility can often be noticed in young children and infants and may hinder gross motor development (crawling, walking)
-
Hypotonia (infants)
-
Low bone density
-
Early onset osteoarthritis
-
Extensive “double-jointedness”
-
Fluid buildup in the joints
-
Frequent, easily broken bones
-
Spinal stenosis
-
TMJ
-
Scoliosis and/or kyphosis
-
-
Tissue fragility
-
Skin fragility (see above)
-
Small blood vessel fragility causes easy bruising and, in children especially, is the presenting symptom when visiting the doctor
-
Repetitive hernia (inguinal, umbilical, hiatal, or incisional)
-
Recurrent rectal prolapse in children
-
-
Cardiovascular manifestations
-
Mitral valve prolapse
-
Spontaneous rupture of large arteries (severe vascular symptoms are associated with vascular EDS
-
Aortic root dilation
-
Blood pressure problems
-
Easy bruising
-
Dysautonomia and POTS (Postural Orthostatic Tachycardic Syndrome)
-
-
Neurological/Psychological
-
Anxiety and Depressive disorders
-
Chronic, widespread musculoskeletal pain
-
Migraine Headaches
-
Decreased deep tendon reflexes
-
Low body temperature
-
Hypotonia (infants)
-
Poor response to local anesthetic
-
-
Pregnancy related
-
Pregnancy in a woman with classic EDS is potentially dangerous for both the mother and child, especially if the fetus is affected
-
Premature rupture of membranes is a common cause of premature delivery
-
Breech position of the fetus is common when the fetus also has EDS
-
Increased risk of tearing of the perineum and extension of episiotomies
-
Uterine and bladder prolapse may occur after delivery
-
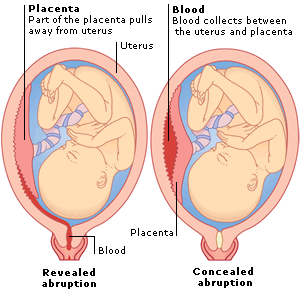
Placental abruption
-
Miscarriages
-
-
Gastrointestinal
-
intestinal rupture
-
Chronic or increased occurrence of constipation
-
Internal organ rupture
-
Acid reflux
-
Hiatal, inguinal, umbilical, or other hernias
-
GI motility syndromes
-
-
Oral/Facial
-
Blue-tinted sclerae
-
TMJ
-
Gum fragility
-
Fragile teeth
-
Myopathy (nearsightedness)
-